Configuring Ethernet Connections
"Extreme" base stations have two ethernet ports. One of these ports on the new base station is for the high-speed connection to you ISP which is called the WAN port. You may connect this port to a router which is connected to your high-speed internet, a hub which attached to a LAN, or directly to a cable or DSL modem. The WAN port has a symbol next to it that looks like a circle of dots.
The other ethernet port is the so-called LAN port. It has a symbol that looks like this <···>, and is meant for your internal network in case you're using the ABS as a router. So if you're planning on attaching the ABS to the cable/DSL modem and hooking up a number of desktops, this is the port you'd want to attach a hub to. Here is how to configure the Ethernet Tab.
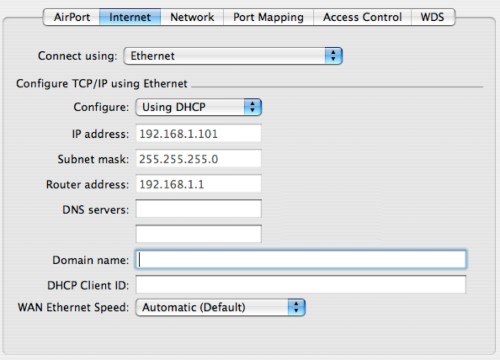
- Set up "Configure TCP/IP:"
- If you are using a cable modem or DSL line, chances are that "Using DHCP" is ideal.
- If your ISP requires a manual configuration, you can select "Manual" instead and enter all the information that your ISP provided to you. This is quite a bit of work and it is imperative that all numbers and points are entered correctly. Otherwise, you are going to be very, very frustrated.
- If you're having frequent issues with flaky internet connections, your base station may be interacting badly with the high-speed modem. Usually, it's a problem that manifests itself with Domain Name Servers (I describe what DNS servers do in a bit more detail on my Drop-Outs Troubleshooting page). If the Domain Name Server (DNS) information is not passed properly between the modem and the base station you'll get frequent messages from your web-browser to the effect of Safari can't find page "http://www.xyz.com/abc.html" because it can't find the server "www.xyz.com".
If this is the case, simply copy the gray IP numbers to the right of the DNS Server fields exactly as shown into the open fields. Be very careful to get this step right... the IP numbers should consist of four sets of digits separated by dots, like "45.91.129.5", as a random example. Enter two different IP addresses for the DNS servers to ensure that if one fails that the other can pick up the load.
If the IP addresses are not listed next to the entry field, call up your ISP to get the information from them or look at your contract (sometimes, the DNS server IP addresses are listed there).
Note: By manually entering IP addresses for the DNS servers, you may experience service issues if the ISP changes the addresses of its DNS servers (typically, this is very rare). On the other hand, entering the DNS addresses can dramatically speed up your browser and may make it more adept at finding the servers you're looking for. I enabled it on my base station because RCN's cable modem misbehaves from time to time and have not had any issues with my browser since then.
- At the bottom of the screen, the admin utility also allows you to enter a DHCP client ID, which your ISP would give to you if it was necessary. Otherwise, just leave it blank.
- Last but not least, you can configure the speed of your WAN ethernet port (the port to which the high-speed modem should be connected). Typically, the setting should be left on Automatic. Should you find that the ABS is not surfing as fast as it should be, you can force it to use 100Mbit/s full-duplex or 10Mbit/s full-duplex. However, most modems today only support 10Mbit/s connections. Forcing the ABS to communicate at a specific speed may thus break your connection!


